Exchange Management Shell, this powerful and amazing tool that comes along with Microsoft Exchange Server 2007 as one of the Two New Administrative Consoles that you can use to administer the entire Exchange 2007 Organization. I will show you, in this article one of the amazing techniques that you can use with Exchange Management Shell to create mailboxes for users that does not have a mailboxes, using one Single Command. EMS will allow you to locate all non-mailbox-enabled users under your active directory domain and immediately create a mailbox for all these users, and even specify under which mailbox store and storage group you want to host these new mailboxes.
I will show you as well, how to locate users based on command shared attributes between some of users and therefore create a mailbox for these users only, Great right :) So let’s start.
I am using one Domain Controller with Exchange 2007 SP1 Server installed to be able to show you with snaps what I am talking about here. I have created Two OU’s, First OU called “Rangers” my community :) , and second OU called “DotNetBoom” , another community “Enemy” :) just kidding. Now, I created new users under each OU without creating a mailbox for them.
Now, I want to locate or list all the users under my “ProRangers.net” domain that do not have mailboxes. In order to do that from Shell Command, I will be using the “Get-User” Command with a special attributes or Filter called “RecipientType” with a value of “User” to search for only non-mailbox users, here is the command:
Get-User l Where-Object{$_.RecipientType –eq “User”}
The output will be a list of all users that do not have a mailbox:

As you can see from the above screen, the command bring all the users under “
prorangers.net” domain that does not have mailbox, even a list of a users that I don’t want to create a mailbox for, like
Guest, Support_XXXXXX, krbtgt, IUSR_XXX, etc. Then what to do?
Ok, lets minimize the result by doing a search for a users that are located under a certain OU. Yes, you can do that, I’ve told you its amazing tools :) . Exchange Management Shell can get a list of all non-mailbox users that are located under certain OU by using
“-OrganizationUnit” attribute along with “
Get-User” Command.
Let’s say I want to get a list of all users located under “
Rangers” OU that does not have a mailbox, here is the exact command:
Get-User –OrganizationalUnit “Rangers” l Where-Object{$_.RecipientType –eq “User”}
Now, look to the output list:

Now, from the above list, you can see that these are my users that are located under my “
Rangers” OU, for which I want to create a mailboxes. Now, lets create amailboxes for all these users under a mailbox store called “
ProRangers Store”. I will use the same upper command to first get the list, then use the output of this list and pipeline it with another command to create the mailboxes for these users under the chosen mailbox store, here is the command:
Get-User –OrganizationalUnit “Rangers” l
Where-Object{$_.RecipientType –eq “User”} l
Enable-Mailbox –Database “ProRangers Store”}And here is the output:

Using Single Shell Command, I could first locate all non-mailbox-enabled users that located under certain OU (
Rangers) and then create a mailbox for them, did you see easier than this before ? I don’t think so :) . Imagine you have hundreds of users , no not hundreds , thousands of users that you want to create mailboxes for them, wouldn’t be easier for you to use such Tool ? I think yes.
Ok, now, lets go beyond this normal search. Lets say that you have single OU , and this OU contains users from multiple departments, and you want to create a mailbox for users from certain department, then my answer to you is “Exchange Command Shell - EMS” offcourse.
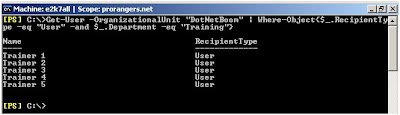
Lets take a look into the following OU called “
DotNetBoom” and notice the Departments column for each user, specially the Users under “
Training” Department:

Now, lets say I want to create a mailbox for those Trainer users who are working under “
Training” Department. So, my command would search for the users under "
DotNetBoom" OU who does not have a mailbox AND have “Training” Value under “Department” Attribute, here I combined two filters, first filter was the users without mailboxes, “AND” then the users that have “
Training” value under “
Department” Attribute. Then the output of this search will be used to “
Mail-Enabled” these users, here is the command:
Get-User –OrganizationalUnit “DotNetBoom” l
where-object{$_.RecipientType –eq “User” -and $_.Department –eq “Training”}And this is the output of this command:
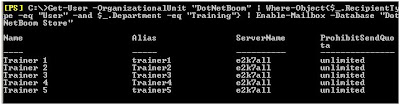
After you found your users or trainers , lets create a mailbox for them, and this time, I will place their mailboxes under another mailbox store called “
DotNetBoom Store”, here is the complete command:
Get-User –OrganizationalUnit "DotNetBoom" l
where-object{$_.RecipientType –eq “User” -and $_.department –eq “Training”} l
Enable-Mailbox –Database “DotNetBoom Store”}And here is the output :
Lets say you want to find your Trainees now that located under your domain if you don’t know where are your trainees located, but you know that they have a title of “
Trainee” under “
Title” Attribute of each user. Lets say I have a trainee under “
DotNetBoom” and “
Rangers” OU’s, and I want to create a mailbox for these trainees, then I would run the following command to find these trainees and create mailboxes for them under a special Mailbox Store created for the Trainees called “
Trainee Store”:
Get-User l
where-object{$_.RecipientType –eq “User” -and $_.Title –eq “Trainee”} l
Enable-Mailbox –Database “Trainee Store”}and here is the output for my trainee located under my domain “
prorangers.net”:

Where,
DTrainee X is located under “
DotNetBoom” OU and
PTrainee X is located under “
Rangers” OU.
Ok, the last thing, I have users with mailboxes and users without mailboxes. Now, I want to create a mailbox for the remaining users across the “
ProRangers” Domain and regardless their OU Location, but based on the following conditions:
·
User does not have mailbox, AND
· Have the word “Community” in their ”Company” Attribute, by using -ilike filter switch.So, here is the command:
Get-User l
where-object{$_.RecipientType –eq “User” -and $_.Company –ilike ‘*Community*’} l
Format-Table Name, RecipientType, CompanyIn the above command, I want the output to show me the name of the user, and the company name that belongs to that user, so I used “
Format-Table” Switch. here is the output of the above command, and check the name of the company for each user, it meets the condition of the command, where the company contains the word “
Community” and these are non-mailbox-enabled users too:

Fine, lets shoot the command that will create mailbox for these users, and locate them under “
ProRangers Store” Mail Store:
Get-User l
where-object{$_.RecipientType –eq “User” -and $_.Company –ilike ‘*Community*’} l Enable-Mailbox –Database “ProRangers Store”}And here is the result,

Now, after we created mailboxes for all usesr using Command Shell, lets see who are the users that don’t have mailbox under “
ProRangers” domain, using the first command at the beginning of this article, which is:
Get-User l
Where-Object{$_.RecipientType –eq “User”}And here is the output of this command:

Now, lets get the users who are “
UserMailbox” Type of users, I will run the same command, but this time with “
UserMailbox” instead of “
User” for the RecipientType Filer, here is the command:
Get-User l
Where-Object{$_.RecipientType –eq “UserMailbox”}And the output this time you will figure it out, when you run this command :) Just hint, you the output should list all Mailbox-Enabled users under your Domain.
I hope that this article was somehow interrested to all of you, and you got something new and amazing by using the amazing tools “
Exchange Management Shell”


















 After you found your users or trainers , lets create a mailbox for them, and this time, I will place their mailboxes under another mailbox store called “
After you found your users or trainers , lets create a mailbox for them, and this time, I will place their mailboxes under another mailbox store called “ Lets say you want to find your Trainees now that located under your domain if you don’t know where are your trainees located, but you know that they have a title of “
Lets say you want to find your Trainees now that located under your domain if you don’t know where are your trainees located, but you know that they have a title of “
 Fine, lets shoot the command that will create mailbox for these users, and locate them under “
Fine, lets shoot the command that will create mailbox for these users, and locate them under “